Genetic Testing Before Pregnancy
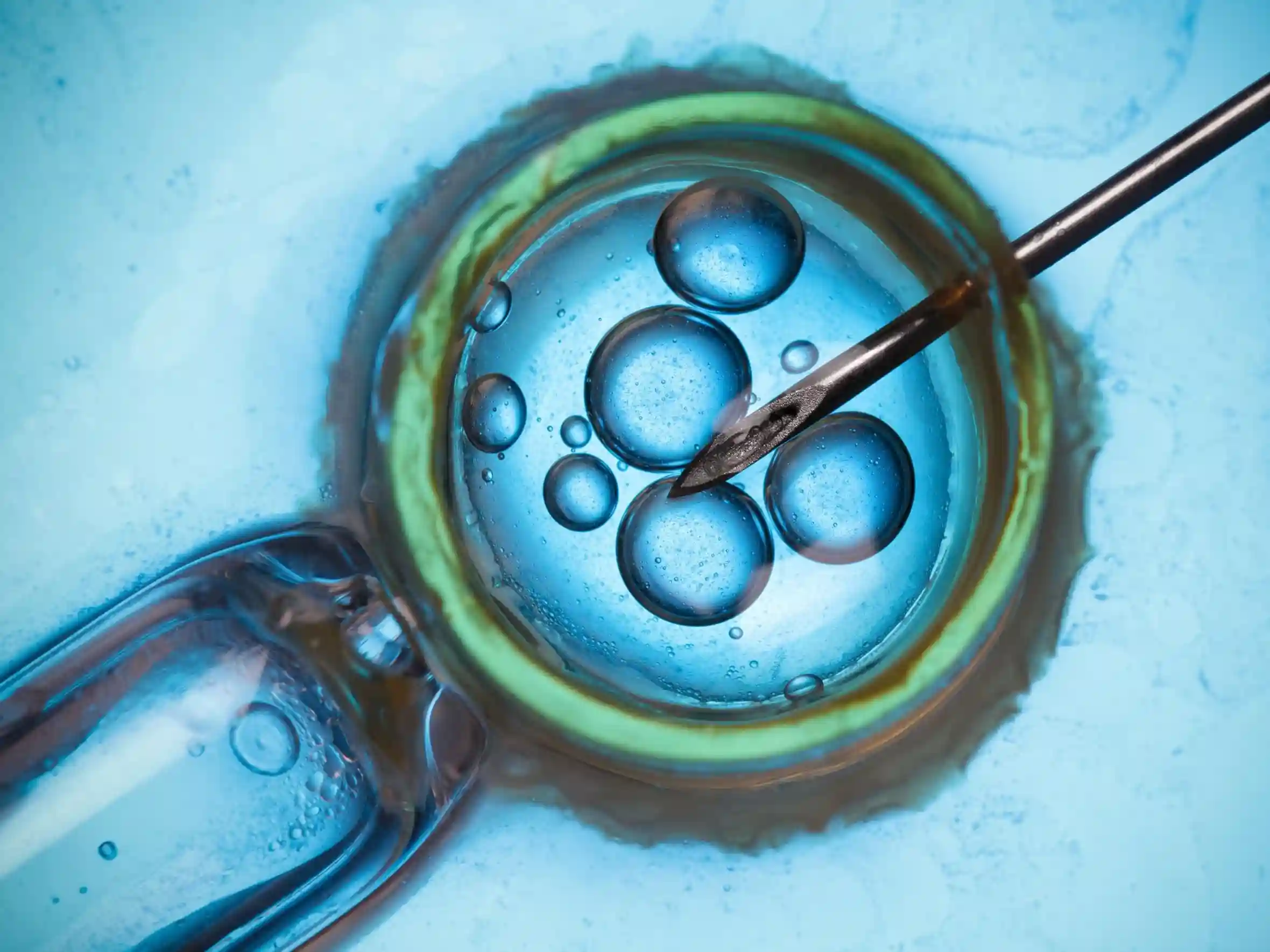
Read about how preimplantation genetic testing works, who it's for, and why it matters. Learn about the benefits and considerations of this cutting-edge fertility tool.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing
In the ever-evolving field of reproductive medicine, Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) has emerged as a beacon of hope for many aspiring parents. This groundbreaking technique offers a glimpse into the genetic makeup of embryos before they’re implanted, potentially increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy and a healthy baby. Let’s embark on a journey to understand the intricacies of PGT and how it might play a role in your path to parenthood.
Decoding the Types of Preimplantation Genetic Testing
PGT-A: Screening for Chromosomal Balance
Imagine being able to peek at the very blueprint of life within an embryo. That’s essentially what PGT-A, or Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy, allows us to do. This test scrutinizes all 23 pairs of chromosomes in an embryo, looking for any numerical abnormalities.
Why is this important? Well, having the correct number of chromosomes – 46 in total – is crucial for healthy development. When there are extra or missing chromosomes, it can lead to various complications, from failure to implant to miscarriage, or even genetic disorders in a future child.
PGT-A is particularly valuable for women over 35, as the risk of chromosomal abnormalities increases with age. It’s like having a skilled detective examine each embryo, helping to select the ones with the best chance of developing into a healthy baby.
PGT-M: Targeting Specific Genetic Conditions
While PGT-A looks at the big picture of chromosomal health, PGT-M (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Disorders) zooms in on specific genetic conditions that might run in a family. Think of it as a customized genetic search-and-identify mission.
For couples who know they carry genes for conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or Huntington’s disease, PGT-M offers a way to significantly reduce the risk of passing these conditions to their children. It’s a powerful tool that can bring peace of mind and help families break the cycle of inherited genetic disorders.
Who Stands to Benefit from PGT?
The beauty of PGT lies in its versatility. While it’s not necessary for everyone, certain groups can benefit immensely from this technology:
- Women over 35 who are trying to conceive often find PGT-A invaluable. As maternal age increases, so does the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs.
- Couples who’ve faced the heartbreak of recurrent miscarriages may find answers and hope through PGT.
- Those with a family history of genetic disorders can use PGT-M to reduce the risk of passing these conditions to their children.
- Individuals or couples who’ve experienced multiple failed IVF attempts might turn to PGT to improve their chances of success.
The Journey Through PGT: What to Expect
Embarking on the PGT process is like setting out on a carefully planned expedition. Here’s what the journey typically looks like:
-
It all begins in the lab, where embryos are cultured to the blastocyst stage – typically 5 to 6 days after fertilization. This is when the embryo has developed enough to allow for safe biopsy.
-
Next comes the biopsy, a delicate procedure where a skilled embryologist carefully removes a few cells from the outer layer of the embryo – the part that will eventually form the placenta. It’s a bit like taking a tiny sample from the embryo’s ‘skin’ without disturbing its core.
-
While these cells are whisked away for genetic analysis, the embryos themselves are carefully frozen, waiting in a state of suspended animation for the results of their genetic ‘report card’.
-
In the genetics lab, the real detective work begins. Scientists meticulously examine the genetic material, looking for any signs of chromosomal abnormalities or specific genetic conditions, depending on whether it’s PGT-A or PGT-M being performed.
-
Once the results are in, typically within 1-2 weeks (though complex cases might take longer), your reproductive specialist will go over them with you. This is where you’ll learn about the genetic health of each tested embryo.
-
Armed with this knowledge, you and your medical team can make informed decisions about which embryo(s) to transfer, optimizing your chances for a healthy pregnancy.
Deciphering PGT Results: What Do They Mean?
When the results come in, they generally fall into one of four categories:
-
Euploid (Normal): These are the star students of the embryo class. With all 23 pairs of chromosomes present and accounted for, these embryos are considered the best candidates for transfer.
-
Aneuploid (Abnormal): These embryos have either too many or too few chromosomes. They’re generally not recommended for transfer as they have a higher risk of implantation failure, miscarriage, or genetic disorders.
-
Mosaic: Think of these as the wild cards. They contain a mix of normal and abnormal cells. The decision to use these embryos is complex and depends on various factors, which your specialist will discuss with you.
-
No Result: Sometimes, the test doesn’t yield a clear result. This could be due to various factors, and your doctor might recommend retesting if possible.
The Promise and the Reality: Benefits and Considerations of PGT
PGT offers several compelling benefits:
- It can significantly increase the chances of a successful pregnancy, especially for those who’ve struggled with fertility issues.
- By identifying chromosomally normal embryos, it can reduce the risk of miscarriage.
- It allows for more confident single embryo transfers, reducing the risk of multiple pregnancies.
- For those at risk of passing on genetic disorders, it provides a way to reduce that risk dramatically.
However, it’s important to approach PGT with a balanced perspective:
- While highly accurate, PGT is not infallible. There’s a small chance of misdiagnosis.
- The process adds to the cost and time of IVF treatment.
- Not all embryos will yield results, which can be emotionally challenging.
Conclusion: Is PGT Right for You?
Preimplantation Genetic Testing is a powerful tool in the realm of reproductive medicine, offering insights that were once impossible to obtain. For many, it has been the key to realizing their dreams of parenthood. However, the decision to undergo PGT is deeply personal and should be made in consultation with a reproductive specialist.
As you consider your options, remember that PGT is just one piece of the fertility puzzle. Your journey is unique, and what works for one couple may not be the best path for another. By staying informed and working closely with your medical team, you can make the choices that are right for you in your quest to build your family.
The field of reproductive genetics is constantly evolving, bringing new hope and possibilities. Who knows what breakthroughs the future might hold? For now, PGT stands as a testament to how far we’ve come in understanding and nurturing the earliest stages of human life.