PCOS and Infertility: Understanding the Connection
Explore the complex relationship between Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and infertility, including its prevalence, symptoms, impact on fertility, diagnosis, and treatment options.
PCOS And Infertility: Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) stands as a prevalent and complex endocrine disorder, impacting millions of women globally. This condition extends beyond its recognizable symptoms, such as irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal disruptions, casting a significant shadow over a woman’s fertility journey. The purpose of this article is to understand the intricate relationship between PCOS and infertility. We will shed light on its underlying causes, diagnostic procedures, and the available treatment modalities.
What Is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevailing endocrine disorder affecting a substantial number of women worldwide. It is characterized by a combination of hormonal imbalances and metabolic disturbances, often manifesting in a range of distressing symptoms.
Prevalence of PCOS: PCOS is remarkably common, with prevalence rates varying across populations and diagnostic criteria. Globally, estimates suggest that it affects 5% to 10% of women of childbearing age. However, these numbers may be higher due to underdiagnosis and variations in diagnostic criteria. It is estimated that PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in Indian women. A study published in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2013 reported that PCOS was responsible for infertility in approximately 70% of women with the condition in India. This study highlights the significant impact of PCOS on fertility among Indian women.
Hormonal Imbalances and Metabolic Disturbances: PCOS is characterized by several hormonal irregularities, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones like testosterone), insulin resistance, and disturbances in gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion. These imbalances contribute to the hallmark features of PCOS.
Common PCOS Symptoms:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Irregular or absent menstrual periods are one of the primary indicators of PCOS. Women with PCOS often experience infrequent, unpredictable, or prolonged menstrual cycles.
- Hirsutism: Excessive hair growth in areas such as the face, chest, and back is common in PCOS, attributed to increased androgen levels.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Elevated androgens can lead to acne breakouts and excessively oily skin.
- Hair Loss: Some women with PCOS may experience thinning hair or hair loss, known as alopecia.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight management and may find it challenging to lose weight due to insulin resistance.
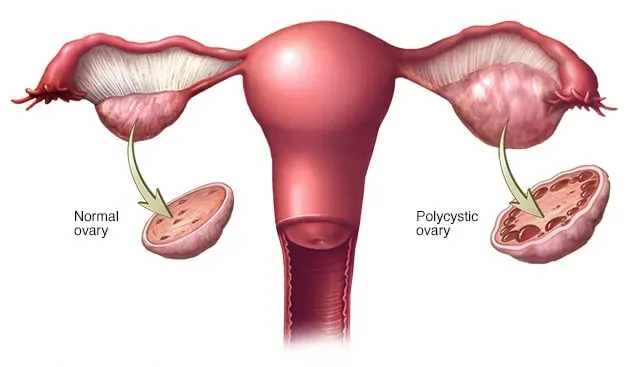
- Polycystic Ovaries: On ultrasound examination, the ovaries of women with PCOS may appear enlarged and contain small cyst-like structures.
Not all women with PCOS will experience the same symptoms, and severity can vary widely. Additionally, PCOS is associated with various long-term health risks, including an increased likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and fertility problems.
Connection Between PCOS And Infertility
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder that exerts a significant influence on a woman’s fertility. Its intricate mechanisms involve disruptions to the normal ovulation process, elevated insulin levels, irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation, and the influence of androgen hormones.
-
Disruption of Ovulation: One of the hallmark features of PCOS is anovulation, where the ovaries do not release eggs regularly. This disruption stems from the abnormal production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Elevated levels of LH relative to FSH, a characteristic of PCOS, can lead to premature egg maturation and a lack of mature follicles. Consequently, ovulation becomes irregular or absent.
-
Role of Elevated Insulin Levels: Insulin resistance is a common metabolic feature of PCOS, affecting up to 70% of women with the condition. Elevated insulin levels stimulate the ovaries to produce excess androgens, particularly testosterone. This excess androgen production contributes to the development of multiple small follicles in the ovaries, often visible on ultrasound as a “polycystic” appearance. High insulin levels can also interfere with normal ovulation and increase the risk of irregular menstrual cycles.
-
Irregular Menstrual Cycles and Anovulation: Women with PCOS frequently experience irregular menstrual cycles, which can range from infrequent periods to prolonged or heavy bleeding. These irregularities are primarily a result of disrupted ovulation. Without regular ovulation, the uterine lining may not develop as expected, leading to unpredictable menstrual patterns. Anovulation, where no egg is released during the menstrual cycle, further contributes to infertility.
-
Impact of Androgen Hormones: Excess androgen hormones, particularly testosterone, can adversely affect fertility. High levels of androgens can disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, leading to ovulatory dysfunction. Androgens can also contribute to the development of conditions like hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and alopecia (hair loss), which are commonly associated with PCOS.
While the specific impact of PCOS on fertility varies among individuals, studies indicate that up to 70% of women with PCOS experience infertility. Addressing PCOS-related infertility often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including lifestyle modifications, medications to induce ovulation, insulin-sensitizing agents, and assisted reproductive technologies like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
PCOS Diagnosis
Diagnosing infertility related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) involves a comprehensive evaluation that considers both the criteria for PCOS diagnosis and the specific challenges it poses to fertility. A thorough diagnostic process is crucial for tailoring effective treatment strategies and maximizing the chances of conception.
Diagnostic Criteria for PCOS: To diagnose PCOS, various criteria are commonly used, including those established by the Rotterdam criteria, Androgen Excess and PCOS Society criteria, and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) criteria. According to the Rotterdam criteria, a woman can be diagnosed with PCOS if she exhibits two out of three of the following features:
- Irregular menstrual cycles or anovulation.
- Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism (elevated androgen hormones like testosterone).
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound examination.
Meeting these criteria is essential for identifying women with PCOS and infertility. However, it is important to note that PCOS-related infertility is a multifactorial condition that requires additional assessments.
Assessing and Diagnosing Infertility: The evaluation of infertility in PCOS patients involves a comprehensive assessment to identify the specific factors contributing to their difficulties in conceiving. This includes:
- Ovulation Assessment: Monitoring menstrual cycles and assessing ovulation patterns is crucial. Anovulation or irregular ovulation is a common feature of PCOS-related infertility.
- Hormone Profiling: Blood tests to measure hormone levels, including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), can provide insights into hormonal imbalances that affect ovulation and fertility.
- Ultrasound Examination: Transvaginal ultrasound can reveal the characteristic polycystic appearance of the ovaries, which may include multiple small follicles.
- Other Diagnostic Tests: Depending on individual circumstances, additional tests such as hysterosalpingography (HSG) to assess tubal patency and semen analysis for the male partner may be performed.
Importance of Comprehensive Evaluation: A comprehensive diagnostic approach is essential because PCOS-related infertility can result from a combination of factors, including ovulatory dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and uterine abnormalities. Tailoring treatment strategies based on the specific findings of the evaluation can significantly improve the chances of successful conception for women with PCOS.
PCOS Treatment Options
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can present unique challenges when it comes to fertility. Fortunately, a range of treatment options is available to help women with PCOS overcome infertility and achieve successful pregnancies. These options encompass lifestyle modifications, medications, insulin-sensitizing agents, assisted reproductive technologies (ART), and surgical interventions. In the context of India, where PCOS is prevalent, addressing PCOS-related infertility is significant.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management: Weight plays a crucial role in PCOS-related infertility. Numerous PCOS patients often encounter insulin resistance, potentially resulting in increased body weight. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can improve ovulation and increase the chances of conception. Indian studies have shown that lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can lead to improvements in insulin sensitivity and fertility in women with PCOS.
- Dietary Changes: A well-balanced diet, rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. Traditional Indian diets that include whole grains, vegetables, and fruits can be beneficial. Research indicates that dietary interventions can improve metabolic and reproductive outcomes in women with PCOS in India.
Medications to Induce Ovulation:
- Clomiphene: Clomiphene citrate is a commonly used medication to induce ovulation in women with PCOS. Studies have demonstrated that Clomiphene can effectively stimulate ovulation, and its use is associated with an increased rate of successful pregnancies in Indian women with PCOS.
Insulin-Sensitizing Agents:
- Metformin: Metformin is an insulin-sensitizing medication often prescribed to women with PCOS. By improving insulin sensitivity, Metformin can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve ovulation. Indian research has shown the benefits of Metformin in improving metabolic parameters and fertility outcomes in PCOS patients.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): In cases where other treatments are ineffective or if there are additional fertility factors at play, IVF can be a highly successful option. Indian studies have indicated that IVF can be particularly beneficial for women with PCOS-related infertility, resulting in a higher rate of successful pregnancies.
Surgical Options:
- Ovarian Drilling: Ovarian drilling is a surgical procedure that involves making small holes in the ovaries using laser or diathermy. This procedure can help restore regular ovulation in some women with PCOS. While ovarian drilling is less commonly performed today due to the success of other treatments, it can still be considered in specific cases.
In India, where PCOS is a prevalent condition, these treatment options are crucial for addressing PCOS-related infertility. The effectiveness of these treatments may vary from individual to individual, and healthcare providers will often tailor treatment plans to meet the specific needs of each patient.
It is essential to consult with a qualified Fertility Doctor for a personalized evaluation and treatment plan. By combining lifestyle modifications, appropriate medications, insulin-sensitizing agents, and, if necessary, advanced reproductive technologies, many women with PCOS can overcome infertility and realize their dreams of motherhood.
Lifestyle And PCOS Management
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes that promote overall well-being and enhance fertility. Here are some practical tips for women dealing with PCOS:
-
Balanced Diet: Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Cut down on processed foods, sugary snacks, and sweetened beverages in your diet. Indian cuisine offers a wide variety of nutritious options, such as lentils, green leafy vegetables, and whole grains like brown rice and millets.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing weight and improving insulin sensitivity. Incorporate exercises like brisk walking, yoga, and strength training into your routine. Indian traditional practices like yoga and meditation can be particularly beneficial for stress management.
-
Stress Reduction: High-stress levels can exacerbate PCOS symptoms and affect fertility. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, or meditation. Traditional Indian practices like Ayurveda and yoga offer effective stress-reduction strategies.
-
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep as it plays a vital role in hormonal balance. Strive to achieve 7-8 hours of peaceful sleep every day.
-
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Herbal teas, such as Tulsi tea, are popular in India and can provide additional health benefits.
-
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your PCOS and its impact on your health. Regular monitoring can help tailor treatment plans to your specific needs.
-
Herbal Remedies: Some Indian herbal remedies, such as fenugreek seeds and turmeric, are believed to have positive effects on PCOS symptoms. Consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating herbal remedies into your routine.
-
Weight Management: If you are overweight, even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can improve PCOS symptoms and fertility. Work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized weight management plan.
-
Medication and Supplements: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for medication or supplements, such as Metformin or inositol, if prescribed.